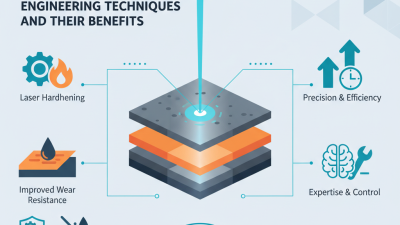
Laser Powder Cladding offers a unique solution for creating advanced material coatings. This technology applies powdered materials using a laser to achieve precise results. It improves surface properties, enhancing wear resistance and corrosion protection.
Many industries benefit from this innovative process. Aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing often use Laser Powder Cladding to extend component life. Applications are diverse, from repairing parts to creating entirely new surfaces. However, achieving consistent quality can be challenging. Each layer must bond effectively, avoiding defects like porosity.
The technology also requires skilled operators. Careful adjustments are necessary for optimal results. Perhaps it’s this complexity that makes some companies hesitant to adopt it. Despite potential drawbacks, Laser Powder Cladding remains a valuable technique for high-performance coatings. Understanding its advantages can lead to better decision-making in material selection.

Laser powder cladding offers significant advantages in advanced material coatings. This technique allows precise delivery of powdered materials onto surfaces. The focused laser beam melts the powder, creating strong bonds as it solidifies. This process enhances the surface properties of various components. For instance, it increases hardness, improves wear resistance, and boosts corrosion resistance.
One of the notable benefits is customization. Users can select different powder compositions based on their specific needs. This flexibility enables tailored coatings that suit unique applications. However, achieving perfect coatings can be challenging. Variations in powder feed rate or laser parameters might lead to defects. Continuous monitoring is crucial to minimize imperfections and ensure optimal results. The learning curve can be steep, but overcoming these hurdles is essential for maximizing performance.
Another advantage is the minimal heat-affected zone. This characteristic preserves the base material's properties. Traditional coating methods often compromise underlying structures. With laser powder cladding, this risk is reduced. Yet, not every application is ideal for this technology. It's essential to assess compatibility with the materials involved. Understanding these factors helps in making informed decisions regarding coating methods.
The laser powder cladding process is gaining traction in manufacturing. This technology utilizes high-powered lasers to fuse fine metal powders onto a substrate. The result is a strong, wear-resistant coating. Researchers report an increase in efficiency of up to 40% compared to traditional methods.
During cladding, the laser melts the powder and substrate surface simultaneously. Cooling occurs rapidly, forming a dense microstructure. Reports indicate that cladding can reduce material costs by 25% due to less waste. However, parameters like laser power and feed rate must be optimized. Often, initial setups require extensive tuning, which can be time-consuming.
Application versatility is a key advantage. Industries ranging from aerospace to automotive can benefit. The technology can enable tailored properties, like corrosion resistance. Notably, some studies show a 30% improvement in lifespan for treated components. Despite these advantages, challenges remain. Mastering the complexity of the process requires skilled technicians.
Laser powder cladding is a cutting-edge technique. It uses powdered material to form a coating on various substrates. This process enhances surface properties. A variety of materials can be utilized in this technique, each with unique benefits and challenges.
Stainless steel is commonly used for its corrosion resistance. It’s durable but can be tricky to handle during the cladding process. Titanium alloys are favored for their lightweight nature. They have excellent strength but can be costly. Carbides and ceramics are also popular options. They provide exceptional wear resistance but might require advanced technology for successful adhesion.
Working with these materials can have setbacks. For instance, the melting point may vary. This leads to challenges in achieving uniform coatings. Furthermore, compatibility with the base material is crucial. Each project may require several trials. It’s essential to learn from these experiences to refine the process continuously. Understanding material properties deeply becomes vital for success in laser powder cladding.
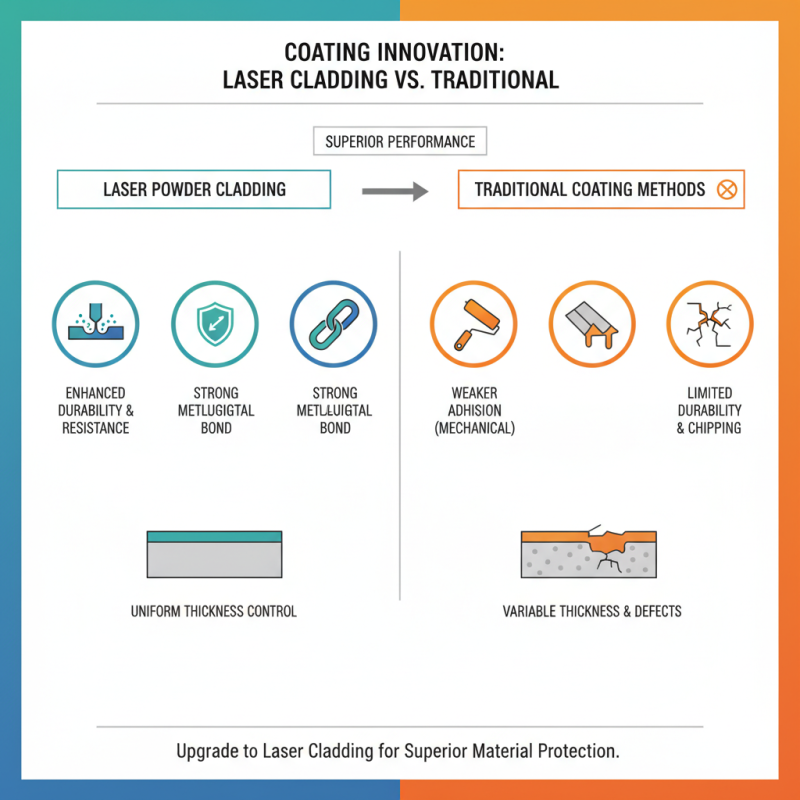
Laser powder cladding offers significant advantages over traditional coating methods. In this process, powdered materials are precisely melted onto surfaces using a laser. This technique ensures a strong bond and enhances durability. Traditional methods, like electroplating or painting, often lead to weaker adhesion and less control over the coating thickness.
One major drawback of traditional coatings is their susceptibility to wear and corrosion. While they may be sufficient for some applications, they don’t provide the same longevity as laser powder cladding. For instance, in harsh environments, traditional coatings can fail quickly. This invites maintenance costs and downtime, which many industries wish to avoid.
Moreover, laser powder cladding enables the application of complex geometries with ease. Intricate designs can be achieved, which is often challenging with conventional methods. However, the initial setup for laser cladding can be expensive. Companies must weigh the costs against long-term benefits. Each choice has implications that require careful consideration.
Laser powder cladding has become crucial across various industries. Its ability to enhance surface properties makes it ideal for different applications. Aerospace and automotive sectors significantly benefit from this technology. It provides a strong, wear-resistant coating that prolongs the life of components. Parts like turbine blades and engine blocks often undergo laser cladding for improved performance.
In addition to aerospace and automotive, the energy sector utilizes laser powder cladding. This technique helps in repairing critical components in power plants. It also enables the creation of complex geometries that traditional methods struggle to achieve. However, it’s essential to understand that not all materials respond equally to cladding. Some materials may present adhesion challenges or brittleness. Consideration of these factors is necessary for successful implementation.
Even industries like medical device manufacturing find value in laser powder cladding. The technology aids in developing custom coatings that can resist corrosion and wear. Biocompatibility is also a concern that requires attention in this field. The journey of adopting laser powder cladding is not without obstacles, and continual refinement is necessary. By addressing these imperfections, companies can harness the full potential of this innovative solution.